Home / 3D anatomy models / 3D anatomical models of pathologies and diseases / Congenital Pulmonary Stenosis
Congenital Pulmonary Stenosis
Congenital Pulmonary Stenosis
 Download a PDF file Add to quotation - wish list
Download a PDF file Add to quotation - wish listProduct description: Congenital Pulmonary Stenosis

Clinical History
This male child had a cardiac murmur discovered at birth. He remained well until the age of 10 months. Two weeks before admission to hospital, he became languid, developed a slight cough, and suddenly gained a lot of weight. Ten days before admission he developed swelling of the hands, feet and face. On examination, he was a chubby child with a blood pressure of 90/59 mmHg. There was a fine thrill over the whole precordium, and a harsh systolic murmur maximal in the pulmonary area. There was oedema of the face and legs. After admission the child gained further weight, and there was no response to therapy. Death was due to congestive cardiac failure.
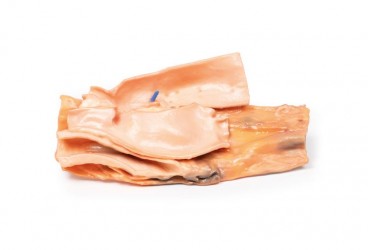
Pathology
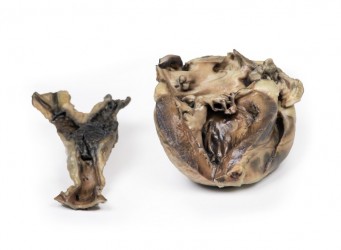
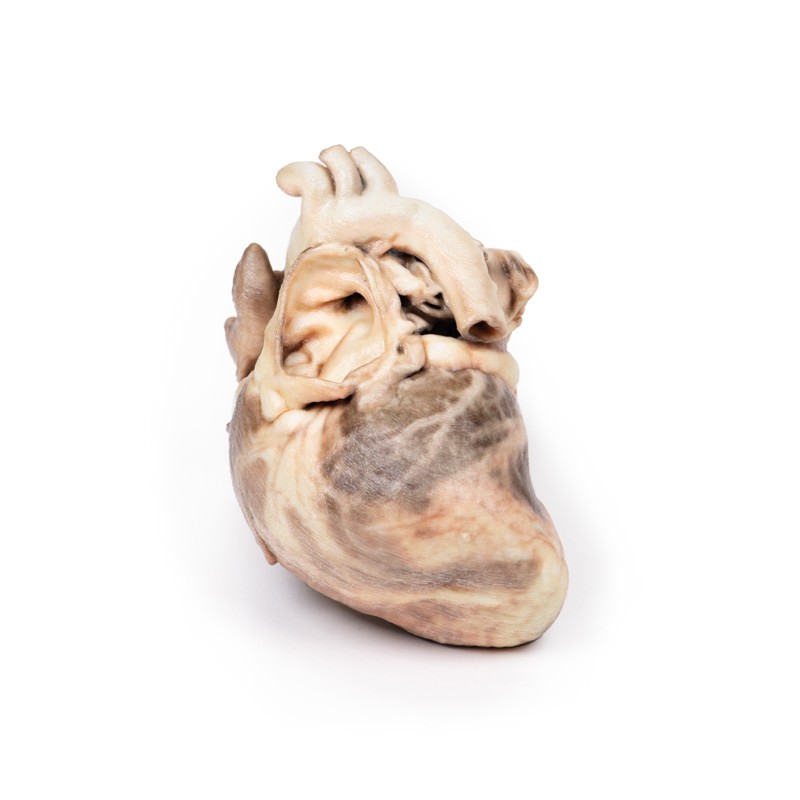
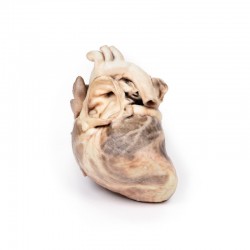
The specimen is the child‘s heart. View from the left side and note the pulmonary artery has been opened to display the upper surface of the pulmonary valve. This abnormal valve consists of a thickened conical diaphragm, with an opening 2 mm in diameter at the apex. The opened pulmonary artery has a large post-stenotic dilatation. There is rightsided cardiac enlargement due to marked dilatation of the right atrium and right auricle (opened), and right ventricular hypertrophy (the wall has been cut in two places [one penetrating, one one not] to expose the hypertrophied myocardium). This is a pure pulmonary valve stenosis.
Further Information
Pulmonary stenosis represents about 7% of congenital heart disease. However, it can also occur later in life secondary to increased pulmonary pressures. In neonates, it may occur as an isolated defect or as part of a more complex lesion, such as the Tetralogy of Fallot. The latter is a combination of four congenital abnormalities, including a ventricular septal defect, pulmonary valve stenosis, a misplaced aorta and a right ventricular hypertrophy. Abnormalities similar to this specimen can now be corrected surgically.
The natural course of congenital pulmonary stenosis varies with age and severity at age of development. Pulmonary stenosis can be thought of on a scale of mild, moderate and severe. While mild pulmonary stenosis can remain asymptomatic and indolent without diagnosis for several years, moderate pulmonary stenosis can rapidly progress to severe stenosis. Severe pulmonary stenosis has significant effects on the heart due to increased pressures leading to right ventricular hypertrophy. Severe pulmonary stenosis is often associated with right ventricular outflow obstruction and subsequent cardiac failure. Thus, moderate to severe pulmonary stenosis may manifest as dyspnoea, chest pain or syncope.
Other complications of severe pulmonary stenosis, include infective endocarditis and arrhythmias caused by remodelling and scarring of the ventricular and atrial walls. Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis is often achieved through transthoracic echocardiography. Other imaging modalities include MRI and CT.